Overview of Liberia
|
|
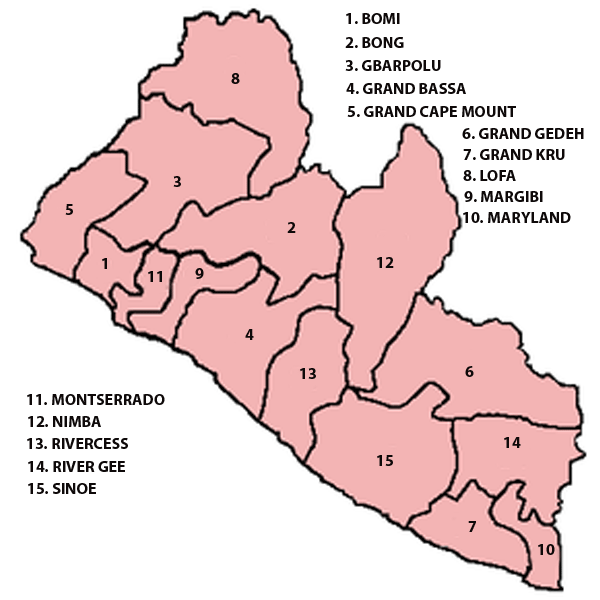
Click image or the name of the counties for details:
Liberia officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Sierra Leone on the west, Guinea on the north and Ivory Coast on the east. Liberia's coastline is composed of mostly mangrove forests while the more sparsely populated inland consists of forests that open to a plateau of drier grasslands.
The country possesses 40% of the remaining Upper Guinean rainforest. Liberia has a hot equatorial climate, with significant rainfall during the May to October rainy season and harsh harmattan winds the remainder of the year.
Liberia covers an area of 111,369 km2 (43,000 sq mi) and is home to about 3.7 million people. English is the official language, while over 30 indigenous languages are spoken within the country.
Along with Ethiopia, Liberia is one of the two modern countries in Sub-Saharan Africa without roots in the European colonization of Africa. Beginning in 1820, the region was colonized by freed American slaves with the help of the American Colonization Society, a private organization that believed ex-slaves would have greater freedom and equality in Africa. Slaves freed from slave ships were also sent there instead of being repatriated to their countries of origin. In 1847, these colonists founded the Republic of Liberia, establishing a government modeled on that of the United States and naming the capital city Monrovia after James Monroe, the fifth president of the United States and a prominent supporter of the colonization. The colonists, known as Americo-Liberians, led the political and economic sectors of the country.
The country began to modernize in the 1940s following investment by the United States during World War II and economic liberalization under President William Tubman. Liberia was a founding member of the United Nations and the Organization of African Unity. A military coup overthrew the Americo-Liberian leadership in 1980, marking the beginning of political and economic instability and two successive civil wars that left approximately 250,000 people dead and devastated the country's economy. A 2003 peace deal led to democratic elections in 2005. Today, Liberia is recovering from the lingering effects of the civil war and related economic dislocation, with about 85% of the population living below the international poverty line.
Counties and districts
Liberia is divided into 15 counties, which are subdivided into districts, and further subdivided into clans. The oldest counties are Grand Bassa and Montserrado, both founded in 1839 prior to Liberian independence. Gbarpolu is the newest county, created in 2001. Nimba is the largest of the counties in size at 4,460 square miles (11,551 km2), while Montserrado is the smallest at 737 square miles (1,909 km2). Montserrado is also the most populous county with 1,144,806 residents as of the 2008 census.
The fifteen counties are administered by superintendents appointed by the president. The Constitution calls for the election of mayors and various chiefs at the county and local level, but these elections have not taken place since 1985 due to war and financial constraints. In 2008, the Supreme Court ruled in favor of allowing the president to appoint mayors until the country could afford to hold municipal elections.
Geography
Liberia is situated in West Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean to the country's southwest. It lies between latitudes 4° and 9°N, and longitudes 7° and 12°W.
The landscape is characterized by mostly flat to rolling coastal plains that contain mangroves and swamps, which rise to a rolling plateau and low mountains in the northeast. Tropical rainforests cover the hills, while elephant grass and semi-deciduous forests make up the dominant vegetation in the northern sections. The equatorial climate is hot year-round with heavy rainfall from May to October with a short interlude in mid-July to August. During the winter months of November to March, dry dust-laden harmattan winds blow inland, causing many problems for residents.
Liberia's watershed tends to move in a southwestern pattern towards the sea as new rains move down the forested plateau off the inland mountain range of Guinée Forestière, in Guinea. Cape Mount near the border with Sierra Leone receives the most precipitation in the nation. The country's main northwestern boundary is traversed by the Mano River while its southeast limits are bounded by the Cavalla River. Liberia's three largest rivers are St. Paul exiting near Monrovia, the river St. John at Buchanan and the Cestos River, all of which flow into the Atlantic. The Cavalla is the longest river in the nation at 320 miles (515 km).
The highest point wholly within Liberia is Mount Wuteve at 4,724 feet (1,440 m) above sea level in the northwestern Liberia range of the West Africa Mountains and the Guinea Highlands. However, Mount Nimba near Yekepa, is higher at 5,748 feet (1,752 m) above sea level but is not wholly within Liberia as Nimba shares a border with Guinea and Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) and is their tallest mountain as well.